Let’s start with the most important information first. There are basically two different types of charging stations: AC charging stations and DC charging stations. So if you are out and about in Switzerland’s well-developed charging network, you have the choice between two different current flows.
What is the difference between AC charging stations and DC charging stations?
The abbreviation AC stands for “alternating current”. DC, on the other hand, is the abbreviation for “direct current”.
AC charging station
- Alternating current →normal charging stations
- Current flows in waves
- Charging power: mostly 22 kW
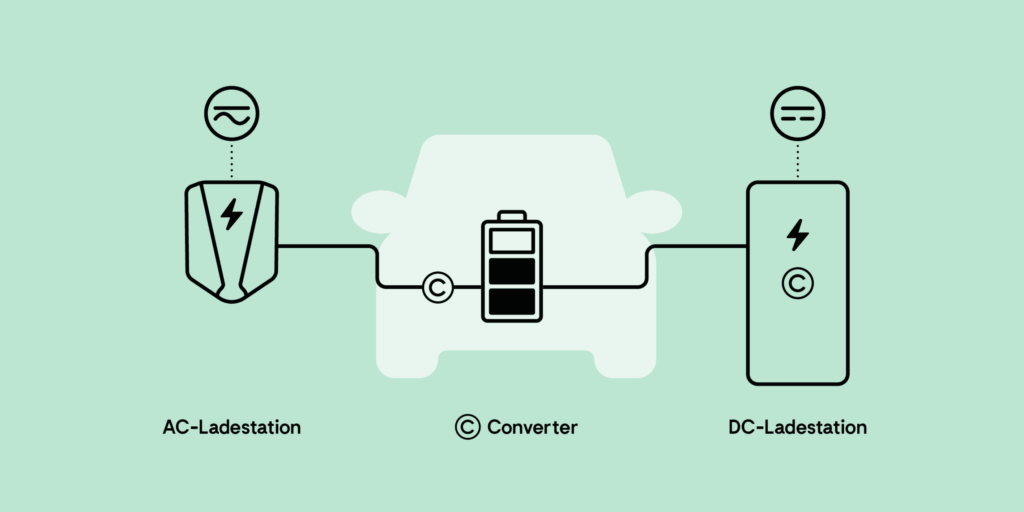
Especially at home, electric cars are charged with alternating current (AC) – for example at wall boxes or at normal safety sockets. But alternating current also flows from public charging stations with type 2 plugs, the most widely used plug in Europe.
Since the battery of an electric car can only store direct current (DC), alternating current is converted during charging via an on-board charger integrated into the electric car.
The result is that the charging process takes longer than at a DC charging station.
DC charging station
- Direct current → fast charging stations
- Current flows in a straight line
- Charging power: up to 350 kW
Public DC charging stations are known as fast charging stations. Here, the alternating current is converted into direct current via a rectifier installed in the charging column and can be charged directly into the battery.
The result is that DC charging creates much higher capacities, which makes the charging process much faster.
AC or DC charging station: which should you choose?
Basically, AC charging is kinder on the battery. However, if you are on a longer road trip or you are again pushed for time, fast charging via a DC charging station is recommended. For everyday life, charging at an AC charging station is recommended if your electric car is stationary for a longer period of time (for example overnight or during work).
Good to know: Find out how to make the most of your charging stops in our article “Charging breaks with the electric car: They really can be that easy”.
Clyde: Your electric car made easy
It’s never been easier to drive your own electric car: Clyde is the most flexible car subscription in Switzerland.
Simply choose the right car and select the desired minimum term between 1 and 48 months as well as the monthly mileage between 250 and 4000 kilometres. You pay a fixed monthly rate that covers all costs for electric cars. The highlight: Public charging is also included in the flat rate price. In addition, Clyde is the only provider where the car is delivered free of charge to any location throughout Switzerland.
Charging is included.
Yes, you read that one right! If you subscribe to an electric car from Clyde, charging is included with our charging flat rate. You can now charge your electric car for free at all available charging stations in the swisscharge.ch network in Switzerland and throughout Europe.


